TechNotes No. 1-1999
Binding
and inhibition of a Concanavalin A — horseradish peroxidase conjugate to a–D–mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates.
Introduction
Binding
of lectins to immobilized saccharides and subsequent inhibition of such a binding
event is often used for evaluating lectin inhibitors. The use of GlycoWell™ plates
facilitates an ELISA assay involving the binding of lectins to the wells. This
TechNote describes the binding and inhibition of a a–D–mannopyranoside
recognizing lectin1, Concanavalin A, to a–D-mannopyranoside GlycoWell™ plates.
Experimental
- Addition of inhibitor.Add to three wells of each GlycoWell™
plate 50µL of inhibitor solution and to three wells of each GlycoWell™ plate 50µL
of TWEEN/PBS.
- Lectin incubation. Add 50µL lectin solution to each well.
Leave for 45 min
- Washing. Empty the wells
and wash three times with CovaBuffer. Leave the last wash in the wells for 15
min. Wash with citrate/phosphate buffer once.
- Substrate
reaction. Add 100µL substrate solution to each well. Read optical density at 490
nm in a microwell plate reader.
Results
The results demonstrate that a a–D-mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plate efficiently binds a mannose–recognizing plant lectin, Concanavalin
A (Figure 1). Thus, GlycoWell™ plates are suitable for detecting carbohydrate
binding properties of proteins. Furthermore, a soluble a–D-mannopyranoside
inhibits the binding of the Concanavalin A–horseradish peroxidase conjugate to
the a–D–mannopyranoside GlycoWell plate,
demonstrating the suitability of using GlycoWell™ plates in competitive inhibition
experiments.
Materials - GlycoWell™
plates SW-00-001 (blank) and SW-01-009 (a–D-mannopyranoside).
- PBS buffer pH 6.8, 0.15 M Na+: 24.0 g NaCl, 0.6
g KCl, 3.46 g Na2HPO4·2H2O, 0.6 g KH2PO4,
3 L H2O.
- TWEEN/PBS:
0.10 mL TWEEN 20, 200 mL PBS.
- CovaBuffer: 116.9 g NaCl,
10.0 g MgSO4·7H2O, 0.50 mL TWEEN 20, 1 L PBS.
- Citrate–Phosphate
buffer, pH 5.0: 7.30 g citric acid, 11.86 g Na2HPO4·2H2O,
1 L H2O.
- Inhibitor solution: 2 mM of 2–(2–carboxyethylthio)–ethyl a–D–mannopyranoside
in TWEEN/PBS.
- Lectin stock: 1.0 mg Concanavalin A–horseradish
peroxidase conjugate (SIGMA L6397), 1.0 mL TWEEN/PBS.
- Lectin
solution: 70 µL Lectin stock, 1.75 mL TWEEN/PBS, filtered through a 0.22 micron
filter.
- Substrate solution: 6.0 mg o–phenylenediamine,
10.0 mL citrate/phosphate buffer, 5 µL H2O2, freshly prepared.
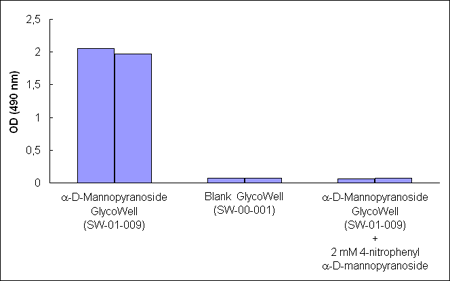 Figure 1. A
Concanavalin A-horseradish peroxidase conjugate binds to a–D–mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-01-009), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). A soluble a–D-mannopyranoside
inhibits the binding of the Concanavalin A–horseradish peroxidase conjugate
to the a–D-mannopyranoside GlycoWell™
plate.
Figure 1. A
Concanavalin A-horseradish peroxidase conjugate binds to a–D–mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-01-009), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). A soluble a–D-mannopyranoside
inhibits the binding of the Concanavalin A–horseradish peroxidase conjugate
to the a–D-mannopyranoside GlycoWell™
plate. |
Reference
1. Reeke, G. N. et al. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.,1974,
234, 369.
 Figure 1. A
Concanavalin A-horseradish peroxidase conjugate binds to a–D–mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-01-009), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). A soluble a–D-mannopyranoside
inhibits the binding of the Concanavalin A–horseradish peroxidase conjugate
to the a–D-mannopyranoside GlycoWell™
plate.
Figure 1. A
Concanavalin A-horseradish peroxidase conjugate binds to a–D–mannopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-01-009), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). A soluble a–D-mannopyranoside
inhibits the binding of the Concanavalin A–horseradish peroxidase conjugate
to the a–D-mannopyranoside GlycoWell™
plate.