TechNotes No. 3-1999
Binding
of plant lectin — horseradish peroxidase conjugate to b–lactoside
GlycoWell™ plates.
Introduction
Binding
of lectins to immobilized saccherides and subsequent inhibition of such a binding
event is often used for evaluating lectin inhibitors. The use of GlycoWell™ plates
facilitates an ELISA assay involving the binding of lectins to the wells. This
TechNote describes the binding of three b–lactose recognizing
lectins, Erythrina cristagalli lectin1, peanut agglutinin2,
and Ricinus communis toxin RCA 1203, to b–lactoside
GlycoWell™ plates.
Experimental
- Lectin incubation.Add 100 µL lectin solution to
each well. Leave for 45 min
- Washing. Empty the wells and
wash three times with CovaBuffer. Leave the last wash in the wells for 15 min.
Wash with citrate/phosphate buffer once.
- Substrate reaction.
Add 100 µL substrate solution to each well. Read optical density at 490 nm in
a microwell plate reader.
Results
The
results demonstrate that b–lactoside GlycoWell™ plate
efficiently binds different b–lactose–recognizing plant
lectins, (Figure 3). Thus, GlycoWell™ plates are suitable for detecting carbohydrate
binding properties of proteins.
Materials
- GlycoWell™ plates SW-00-001 (blank) and SW-02-001 (b–lactoside).
- PBS
buffer pH 7.2, 0.15 M Na+: 24.0 g NaCl, 0.6 g KCl, 3.46 g Na2HPO4·2H2O,
0.6 g KH2PO4, 3 L H2O.
- TWEEN/PBS:
0.10 mL TWEEN 20, 200 mL PBS.
- CovaBuffer: 116.9 g NaCl,
10.0 g MgSO4·7H2O, 0.50 mL TWEEN 20, 1 L PBS.
- Citrate–Phosphate
buffer, pH 5.0: 7.30 g citric acid, 11.86 g Na2HPO4·2H2O,
1 L H2O.
- Lectin stock: 1.0 mg of lectin [E.
cristagalli–horseradish peroxidase conjugate (SIGMA L9050), peanut agglutinin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugate (SIGMA L7759), RCA120–horseradish peroxidase conjugate (SIGMA
L2758) in 1.0 mL TWEEN/PBS.
- Lectin solution: 70 µL Lectin
stock, 1.75 mL TWEEN/PBS, filtered through a 0.22 micron filter. In most cases
the concentration of lectin must be optimized to obtain good readings
- Substrate
solution: 6.0 mg o–phenylenediamine, 10.0 mL citrate/phosphate buffer,
5 µL H2O2, freshly prepared.
- 1 M H2SO4
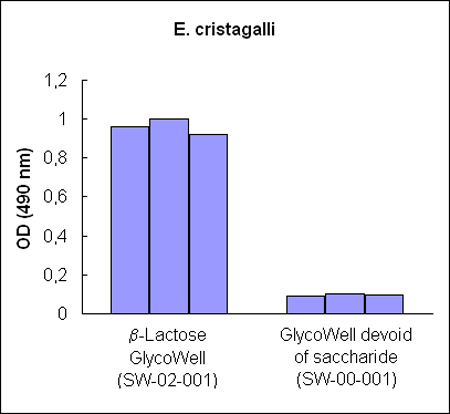
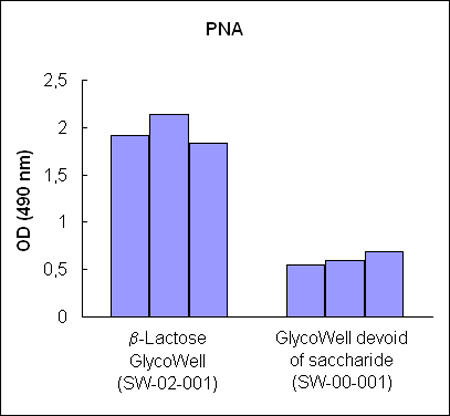 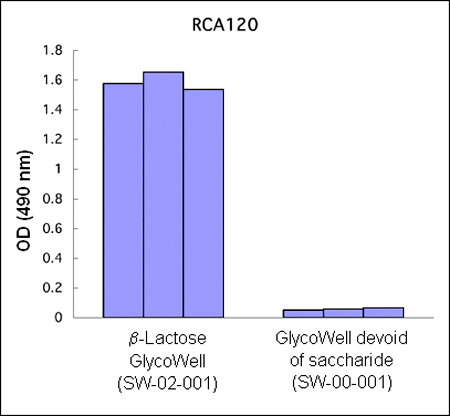 Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001).
Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). |
Reference
1. Iglesias, J.L., Eur. J. Biochem., 1982, 123,
247.
2. Bird, G.W.G., Vox Sang., 1964, 9, 748.
3. Nicolson,
G.L. and Blaustein, J. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1972, 266, 543.


 Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001).
Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001). 

 Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001).
Figure 1:
Three different b–lactoside–recognizing lectin–horseradish
peroxidase conjugates bind to b–D–lactopyranoside
GlycoWell™ plates (SW-02-001), but not to a GlycoWell™ plate devoid of
saccharide (SW-00-001).