TechNotes No. 5-1999
Binding and inhibition P-fimbriated uropathogenic E.
coli to b–globotetraoside GlycoWell™ plates.
Introduction
Human P-fimbriated uropathogenic Escherichia coli bacteria
express a carbohydrate-specific adhesin protein, which is believed to be an important
virulence factor. The endogenous carbohydrate ligand for this adhesin in globotetraose
(Gb4, b–D–GalNAc–(1-3)–a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Glc)1. The submolecular details
of the carbohydrate epitope of this adhesin have been investigated by inhibiting
the bacteria binding to a Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate with synthetic carbohydrate analogs
of Gb42. This TechNote describes the binding of P–fimbriated E.
coli to Globotetraose GlycoWell™ plates, as well as competitive inhibition
using a soluble derivative of the central disaccharide of Gb4, galabiose (a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3)3,
as inhibitor.
Experimental
- Bacteria preparation. Grow the bacteria on TS agar
with 100 µg/mL Carbenicillin and passage for 3 days. Suspend bacteria in PBS to
an A540 of 1.0. Spin down a know volume of the bacterial suspension
and resuspend the pellet in PBS containing 2 % BSA (1/20th of the original volume).
Use this bacterial suspension in the experiment described below.
- Blocking
for non-specific binding. Block the wells for non-specific binding by incubation
overnight at 4şC with 400 µL of PBS containing 2% BSA and E. coli cells
devoid of adhesin suspended to a klett of 50. Wash three times with PBS and leave
the last portion of washing for 15 min in the wells.
- Addition
of inhibitor. Add to three wells of Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate 50µL of inhibitor
solution and to three wells of Globotetraose GlycoWell™ plate 50µL of PBS. Add
to three wells of N–acetyl (blank) GlycoWell plate 50µL of PBS.dilution
series. Dissolve the inhibitor to 18 mM in PBS. Dispense 75 µL of inhibitor
solution to the first well of Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate. Dispense 50 µL of PBS to all
other wells. Make serial three–fold dilutions by transferring 25 µL from the first
well to the second well, mixing, transferring 25 µL from the second well to the
third, and so on until the eleventh well. Remove and discard 25 µL from the eleventh
well. The very last well (twelfth) will contain no inhibitor. Make the inhibitor
dilution series in triplicate.
- Bacteria incubation. Add
50 µL bacteria suspension (HB101/pPAP5) to all wells except control wells. Add
50 µL bacteria (HB101/pPAP24) devoid of papG adhesin to control wells. Shake the
plate gently. Incubate for 45 min at room temperature.
- Washing.
Empty the wells and wash three times with CovaBuffer. Leave the last wash in the
wells for 15 min.
- Incubation with 1° antiserum. Add
100 µL anti–pili rabbit antiserum solution. Incubate for 60 min at room temperature.
- Washing.
Empty the wells and wash three times with CovaBuffer. Leave the last wash in the
wells for 15 min.
- Incubation with 2° antiserum Add
100 µL alkaline phosphatase–conjugated anti–rabbit IgG solution. Incubate for
60 min at room temperature.
- Washing. Empty the wells
and wash three times with CovaBuffer. Leave the last wash in the wells for 15
min. Wash once with substrate buffer.
- Substrate incubation.
Add 100 µL of substrate solution to each well. Read OD at 405 nm in a microwell
plate reader. Subtract the optical density reading from control wells (incubated
with HB101/pPAP24) from the optical density reading from other wells.
Results
The results demonstrate that a Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate provides high signal–to–noise
ratios in competitive ELISA experiments. The binding and inhibition of P–fimbriated
E. coli to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates constitute a simple and reproducible assay
for evaluating competitive inhibitors (Figure 1).
Materials
- PBS buffer pH 7.2, 0.15 M Na+: 24.0 g
NaCl, 0.6 g KCl, 3.46 g Na2HPO4·2H2O, 0.6 g KH2PO4,
3 L H2O.
- CovaBuffer: 116.9 g NaCl, 10.0 g MgSO4·7H2O,
0.50 mL TWEEN 20, 1 L PBS.
- Gb4 (SW-04-001) plates.
- Inhibitor:
(a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3)3.
- E.
coli bacteria4 expressing the PapG adhesin (HB101/pPAP5).
- E.
coli bacteria5 devoid of the PapG adhesin (HB101/pPAP24).
- TS
agar.
- Carbenicillin.
- Bovine Serum
Albumin (BSA).
- Anti-pili rabbit antiserum (WU93 diluted
1/200 in 2% BSA/PBS).
- Alkaline phosphatase–conjugated anti–rabbit
IgG (Sigma A7539, diluted 1/500).
- Substrate buffer: 10%
diethanolamine, 0.5 mM MgCl2, pH 9.4.
- Sigma 104 phosphatase
substrate (i.e. p-nitrophenyl phosphate).
- Substrate
solution: 1 mg/mL Sigma 104 phosphatase substrate in substrate buffer filtered
through 0.22 µM filter.
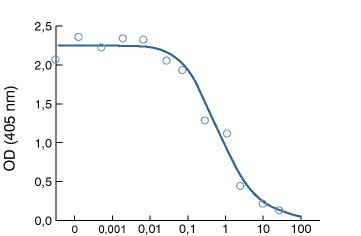 Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.
Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.
|
References
Leffler,
H., Svanborg-Edén, C. FEMS Lett., 1980, 8, 127Nilsson,
U., Striker, R. T., Hultgren, S. J., Magnusson, G. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
1996, 4, 1809K. Jansson, S. Ahlfors, T. Frejd, J.
Kihlberg, G. Magnusson, J. Dahmén, G. Noori, K. Stenvall, J. Org. Chem.,
1988, 53, 5629.Lindberg, F., Lund, B., Normark,
S. EMBO J., 1984, 3, 1167Lindberg, F., Lund,
B., Normark, S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1986, 83, 1891
 Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.
Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.
 Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.
Figure 1.
P–fimbriated uropathogenic E. coli binds to Gb4 GlycoWell™ plates (SW-04-001).
A soluble disacchride fragment of Gb4, galabiose [a–D–Gal–(1-4)–b–D–Gal–OCH2CH2SiMe3],
inhibits binding of the bacteria to the Gb4 GlycoWell™ plate.